資料ライブラリ

アプリケーション・ノート使用上の注意
本アプリケーションノートの英語以外の言語への翻訳はユーザの便宜のために提供されるものであり、リビジョンが古い場合があります。最新の内容については、必ず最新の英語版をご参照ください。
なお、日本語版のアプリケーションノートは基本的に「Rev.0」(リビジョン0)で作成されています。

AN-2594: ADRV904x のSERDES チューニングに関するアプリケーション・ノート
はじめに
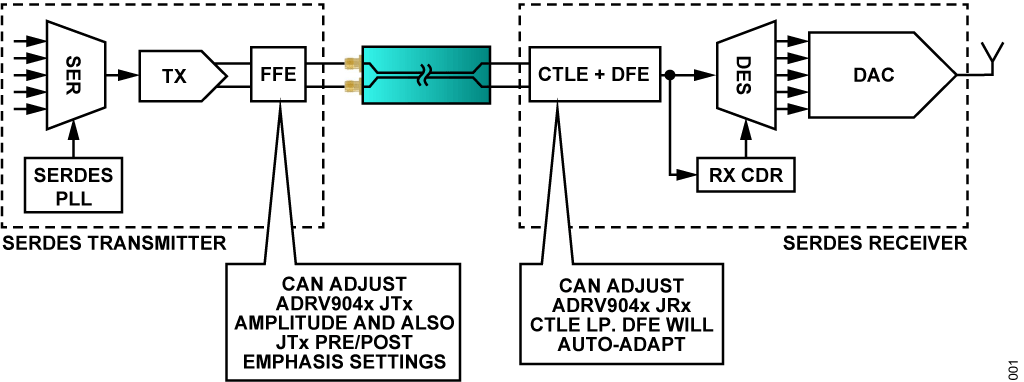
ADRV904x デバイスは、JESD204B/JESD204C 規格に基づくSERDES 高速シリアル・インターフェースを使用して、トランシーバ・デバイスとベースバンドIC(BBIC)との間、またはフィールド・プログラマブル・ゲート・アレイ(FPGA)との間で、A/D コンバータ(ADC)とD/A コンバータ(DAC)のサンプルを転送します。ADRV904x のデシリアライザJRx 側にあるPHY ブロックは、時間連続リニア・イコライザ(CTLE)とデシジョン・フィードバック・イコライザ(DFE)を使用して、損失の大きいチャンネルを通過した後のシリアル・ビットを正しくデコードします。
様々なレーン・レートで最大限の性能を引き出すには、CTLEとDFE を慎重にキャリブレーションする必要がありますが、これはADRV904x のファームウェアによって自動的に行われます。ユーザは、シリアライザJTx の振幅とプリエンファシス設定、およびデシリアライザJRx のCTLE フィルタ設定をチューニングして、図1 に示すように、そのチャンネルの特性に応じてリンクを最適化することができます。このアプリケーション・ノートでは、ADRV904x デバイスの特性評価を行う際に推奨される、SERDES チューニングのプロセスについて説明します。
SERDES リンクのブロック図
DFE の基本
ADRV904x のSERDES レシーバは、CTLE とDFE の両方を1 個ずつ内蔵しています。CTLEはいくつかのフィルタリング段で構成されています。これらの段はチャンネル応答をイコライズするために使われ、そのほとんどは自動的に調整されますが、以降のセクションに示すようにローパス・フィルタ(LPF)段はユーザが設定できます。DFE は、隣接するサンプル点同士のシンボル間干渉(ISI)を計算し、これを除去することによって機能します。DFE の係数はADRV904x のSERDES トラッキング・キャリブレーションによって計算され、自動的に調整されます。更にDFE は、ビットが1 か0 かを判定するデータ・コンパレータのセットと、エラー情報を取得してサンプリング点を最適化するコンパレータも内蔵しています。これらのコンパレータ閾値とその他のDFE キャリブレーション情報は、以降のセクションで説明するSERDES ヘルス・メトリクス・アプリケーション・プロセッサ・インターフェース(API)によってリードバックできます。
SERDES リンク・チューニング
ADRV904x デバイスは、内部CTLE 帯域幅設定、コンパレータDC オフセット、閾値などのパラメータを調整することによって、SERDES PHY ブロックの初期キャリブレーションを実行し、CTLE およびDFE ブロックの適切な設定を決定します。これは、デバイス個々の変動を調整して、ISI のある状態で受信したアイを最適化する助けとなります。
トラッキング・キャリブレーションは、温度や電圧が変動しても性能を維持できるように、通常動作時にも実行されます。トラッキング・キャリブレーションはバックグラウンドで動作し、CTLE とDFE のビット・エラー・レート性能を維持しながら、そのパラメータを微調整します。
キャリブレーションの設定は、使用するSERDES のレーン・レートに応じ、ソフトウェアにより主にデフォルトで行われますが、例えば16G 動作と24G 動作ではデフォルトのパラメータが異なります。これらのキャリブレーション設定のデフォルト値は、アナログ・デバイセズ内部で行われる特性評価に基づいて選ばれます。しかし、配線パターン長とそれに伴う挿入損失の変動はそのプリント回路基板(PCB)固有のSERDES レーン・レイアウトによって決まるので、これらの変動に対応できるように設定を変更できる余地を残しておく必要があります。この調整をできるだけ容易にするために、ADRV904x シリーズのデバイスにはそれぞれのレーン・レートにおける挿入損失に応じて調整が必要なパラメータが1 つあります。
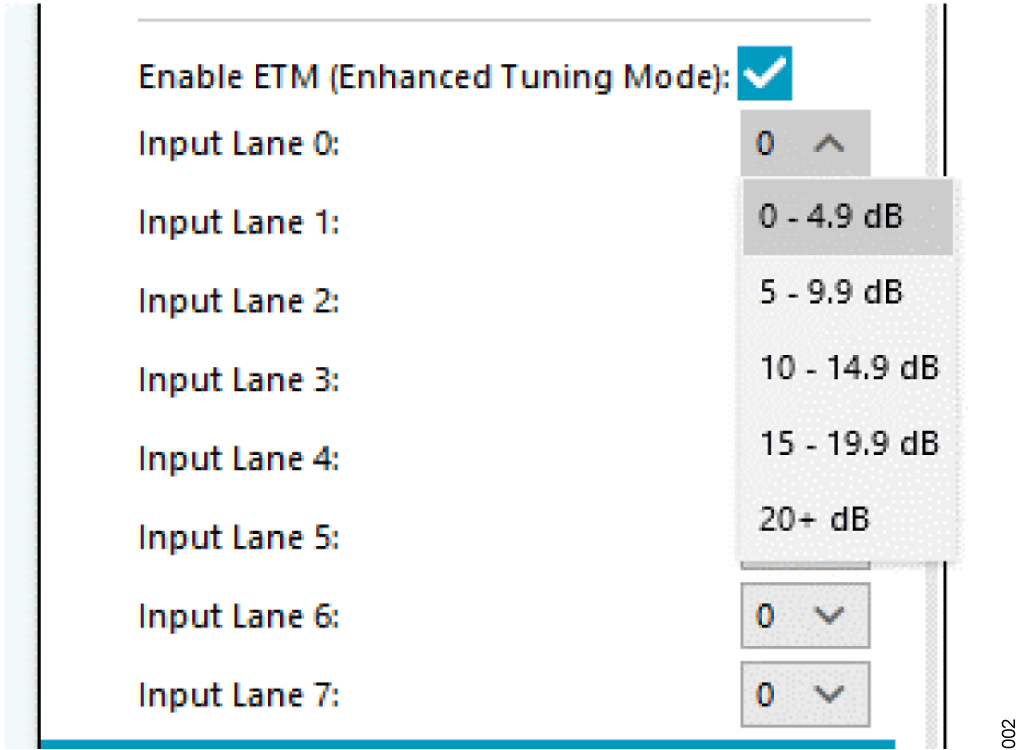
これをイネーブルするには、基本的なJESDの分析、制御、評価(ACE)用グラフィック・ユーザ・インターフェース(GUI)にあるJESD デフレーマ・セクションでEnable ETM (Enhanced Tuning Mode)を選択して、レーンごとに挿入損失範囲を入力します。この挿入損失のプルダウン・リストを図2 に示します。対象レーンの挿入損失範囲が2 つのセクションにまたがる場合、例えば4dB~7dBの場合は、最も近い値の範囲を先に入力します。SERDES リンク・チューニングのセクションに示すように、挿入損失範囲の他の値をテストして比較することができます。更にこの挿入損失範囲は、表1 に示すように、SERDES レーンのレートに応じてlpfMask 値に変換されます。
| SERDES Lane Insertion Loss | 16 G | 19 G | 24 G | 32 G |
| 0 dB to 5 dB | Super Low | Low | Low | High |
| 5 dB to 10 dB | Low | Low | Low | High |
| 10 dB to 15 dB | Low | Med | Med | N/A |
| 15 dB to 20 dB | Med | High | High | N/A |
| 20 dB+ | High | High | High | N/A |
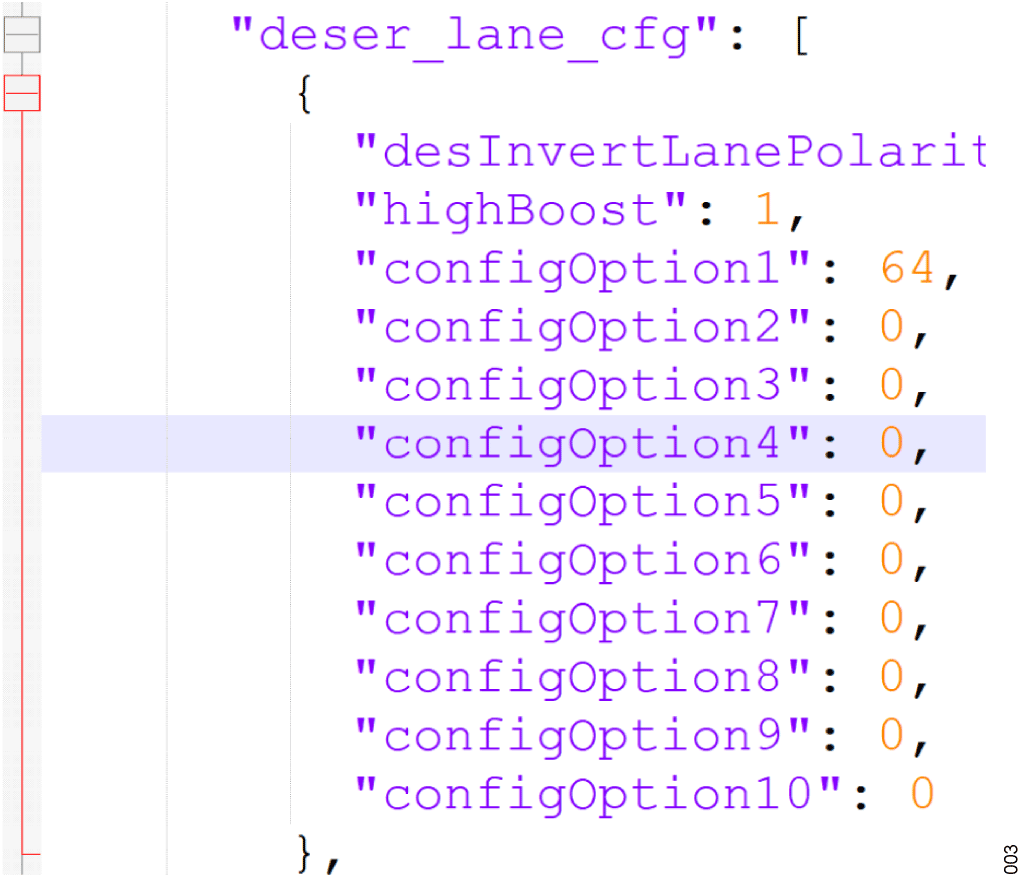
表2 は、与えられたlpfMask に対して設定される10 進値です。この設定はレーンごとに行えます。例えば、いくつかのレーンをlpfMask = Low とし、いくつかのレーンをlpfMask = Mediumとする必要があるような場合です。
| CTLE Bandwidth Setting | LPFMask Value to Program (Decimal) |
| Super Low | 64 |
| Low | 1 |
| Medium | 2 |
| High | 4 |
この値はGUI/コンフィギュレータによって自動的にJSONファイルに書き込まれ、レーンごとにJSON のdeser_lane_cfg セクションにあるconfigOption1が編集されます。例えば、16Gbps時の全レーンの挿入損失範囲が0dB~5dBに設定されている場合、コンフィギュレータは8 つのレーンに"configOption1": 64 を書き込みます。highBoost パラメータもコンフィギュレータによって1 に設定する必要があります。アナログ・デバイセズによって構成が設定されている場合を除き、highBoost やconfigOptionsの設定を手動で行う必要はありません。
レーン・レートが16Gbps 未満の場合のJSONファイル設定
SERDES レーン・レートを16Gbps 未満に設定する場合は、より単純なCTLE およびDFE キャリブレーションが使われます。この場合、SERDES 拡張チューニングは適用されず、すべてのhighboost とconfigOptions の各値を0 に設定して、Enable ETM(Enhanced Tuning Mode)のチェック・マークを外したままにしておくことができます。その場合でも、SERDES 起動シーケンスの一部として、また、この設定での通常動作として、SERDES InitCal を実行し、SERDES TrackingCal をイネーブルする必要があります。
例外の1 つはチャンネルが短い場合で、この場合は、挿入損失が、表3 に示す所定のSERDES レーン・レートに対してユーザ・ガイドに示された最小値未満になります。チャンネルの挿入損失が最小値未満の場合、例えば12Gbps での挿入損失が4dB未満の場合は、以下の設定を手動でJSON ファイルに適用できます。これは、使用中のレーンの一番下のレーンに加えます。例えば、SERDINレーン2/レーン3/レーン4/レーン5/レーン6/レーン7 を使用している場合は、以下のように、JSONファイルのdeser_lane_cfg セクションにあるレーン2 の位置にこれらの値を加えます。
- highBoost:19
- configOption1:78185384
| SERDES Lane Rate (Gbps) | Min Return Loss (dB) | Max Insertion Loss (dB) |
| 8 | 3 | 15 |
| 12 | 4 | 17 |
| 14 | 4.5 | 17 |
16Gbps 未満で低挿入損失のチャンネルについて示した表3 のチューニング・オプションに加えて、SERDES トランスミッタ側のチューニングも実行できます。例えばFPGA で、最良のアイが得られるよう振幅およびプリエンファシスの設定を最適化するには、自動化されたeyeSweep ルーチンを実行し、RunVerticalEyeSweep_v2() APIを使ってeyeHeightおよびeyeWidthデータを得ることができます。
レーン・レートが16GBPS を超えるSERDESキャリブレーション・メトリクス・リードバック用にリンク・チューニングを実行するためのシーケンス
SERDES リンクの確立後、つまりSERDES のInitCal が問題なく実行されてトラッキング・キャリブレーションがイネーブルされた後は、以下のヘルス・メトリクスAPI を通じてキャリブレーション・パラメータをリードバックできます。
- SerdesInitCalStatusGet()
- SerdesTrackingCalStatusGet()
どちらのAPI も様々なキャリブレーション・メトリクスを含む構造を返し、これらはシステム上のファイルに保存したり書き込んだりすることができます。対象となるパラメータを表4 に、返されるメトリクスのすべてのリストをAPI 機能のセクションの表6 と表7 に示します。リンクを介してUserData を送信するときは、SERDES メトリクスをリードバックできます。なお、リンク・チューニングを行うときは、疑似乱数バイナリ・シーケンス(PRBS)データの使用を推奨します。これは、自動化されたeyeSweep ルーチンを実行し、API のRunVerticalEyeSweep_v2()を使ってeyeHeight とeyeWidth のデータを得ることもできるからです。
| InitCal StatusGet フィールド | 基本的な説明 |
| InitCalStatus.temperature | initCal を実行する温度 |
| InitCalStatus.spoLeft | アイ開口部の左側にある位相の数。spoLeft + spoRight は水平方向のeyeWidth を与えます。 |
| InitCalStatus.spoRight | アイ開口部の右側にある位相の数。spoLeft + spoRight は水平方向のeyeWidth を与えます。 |
| InitCalStatus.innerUp | 値(1 − b1)。この値はフェーズ・ディテクタの値に近くなければなりません。 |
| InitCalStatus.innerDown | 値−(1 − b1)。 |
| InitCalStatus.outerUp | 値(1 + b1)。この値は最大信号振幅に相当します(これらb の値がすべて正の場合)。 |
| InitCalStatus.outerDown | 値(1 + b1)。 |
| InitCalStatus.b[7:0] | DFE が計算したカーソル前後のb の値。これらは、ISI を除去するためにデシジョン・フィードバック・イコライザで使われます。 |
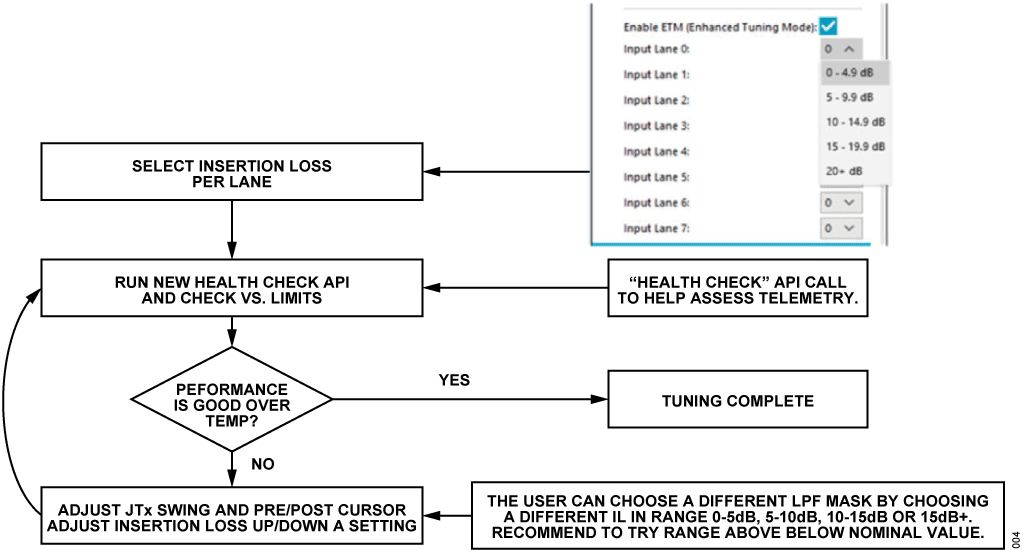
SERDES メトリクス・リミットによる疑似コードのチェック
数多くのパラメータがAPI を介して返されますが、ユーザはその一部を使えば、アイ・メトリクスが良好かどうかを迅速に判断できます。これらは、リンクが良好な状態か、あるいは再チューニングが必要かを判定するために追加する必要のある推奨リミット・チェックです。
このチューニング・プロセスを示すフロー図を図4 に示します。
- チェック1
if (abs(InitcalStatus.outer► Up) >= 63 AND abs(InitcalStatus.outer► Down) >= 63): then check_sat=1 print('DFE is near saturation, consid► er lowering LPF bandwidth or incident sig► nal swing') - チェック2
if (abs(float(calStatus.b[1])/float(calSta► tus.b[0])) < 0.1): then check_isi=1 print ('ISI on channel is too low, consid► er increasing ISI by lowering CTLE LPF band► width') - チェック3
if ((calStatus.spoLeft < 5) OR (calSta► tus.spoRight < 5)): then check_horizontal = 1 print('Horizontal eye open► ing is too low, consider rais► ing FPGA JTx signal swing or increas► ing CTLE LPF bandwidth') - チェック4
If (runEyeVerticalSweepResp.eyeHeight[i] - runEyeVerticalSweepResp.eyeHeight[i+1]) < 20: Then check_eyeHeight = 1 print(‘Vertical eye opening is too low, con► sider raising FPGA JTx signal swing or in► creasing CTLE LPF bandwidth) - チェック5
If (abs(calStatus.b[3]) | abs(calSta► tus.b[4]) | abs(calStatus.b[5]) | abs(calSta► tus.b[6]))>= 8: check_postCursors=1 print ('Post cursor on channel is higher than expected, consider lowering CTLE LPF bandwidth') - 判定チェック
If (check_sat OR check_isi OR check_hori► zontal OR check_eyeHeight OR check_postCur► sors) == 1: Then print "Tuning needed" Else print "No tuning needed"
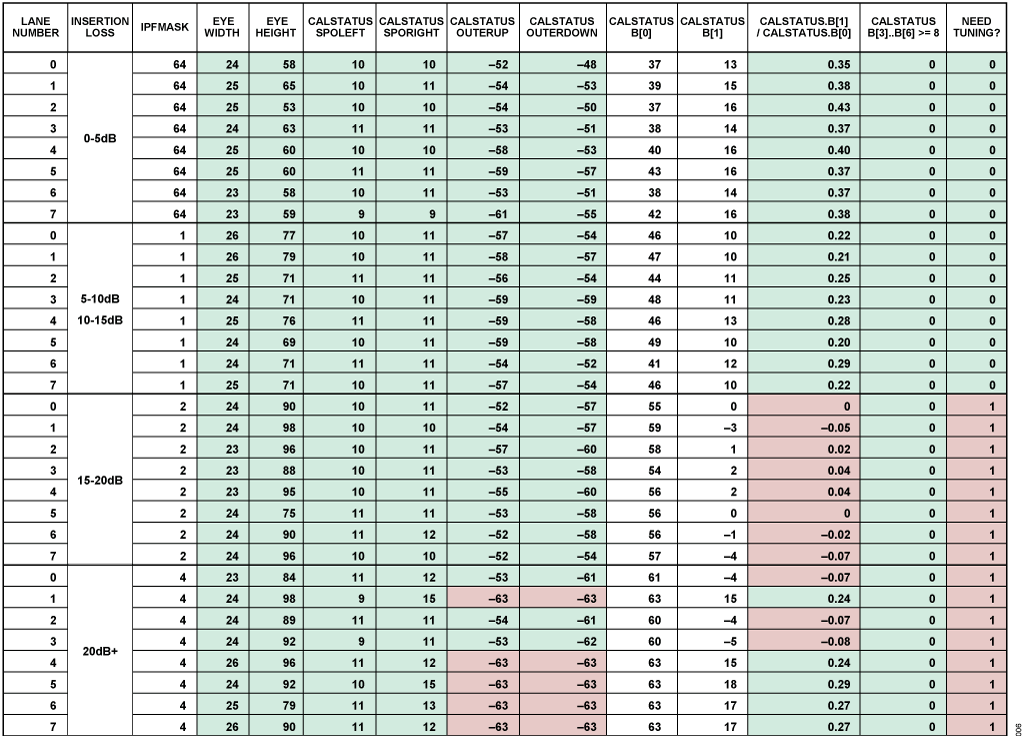
出力データの例を図5 に示します。ここでは16G SERDES の使用事例が選択されており、挿入損失のドロップダウン範囲を調整することにより4 つのlpfMask 設定を通じてスイープが実行されます。lpfMask 設定はC 列に記録されます。4 つのチェックは「CALSTATUS B[3]_B[6] ≥ 8」列に表示され、合格の場合は緑、不合格の場合は赤でハイライトされます。この測定ではチェック5 は省略されています。チェック結果の論理OR(例えば判定チェック)は最後の「Need Tuning?」列に示され、0 は合格、1 は不合格を示します。eyeHeight とeyeWidth だけを合否基準として考えた場合は、4 つのlpfMask 設定のすべてが合格となります。しかし、他の3 つのチェックを考慮した場合、2 と4のlpfMask 設定はすべてのレーンで不合格となります。つまり、該当する挿入損失を使ってアナログ・デバイセズの評価用ボード上で行うこの測定では、lpfMask の値を64(非常に低い)または1(低い)とすることが推奨されます。
様々な温度でのリンク・チューニングの実行
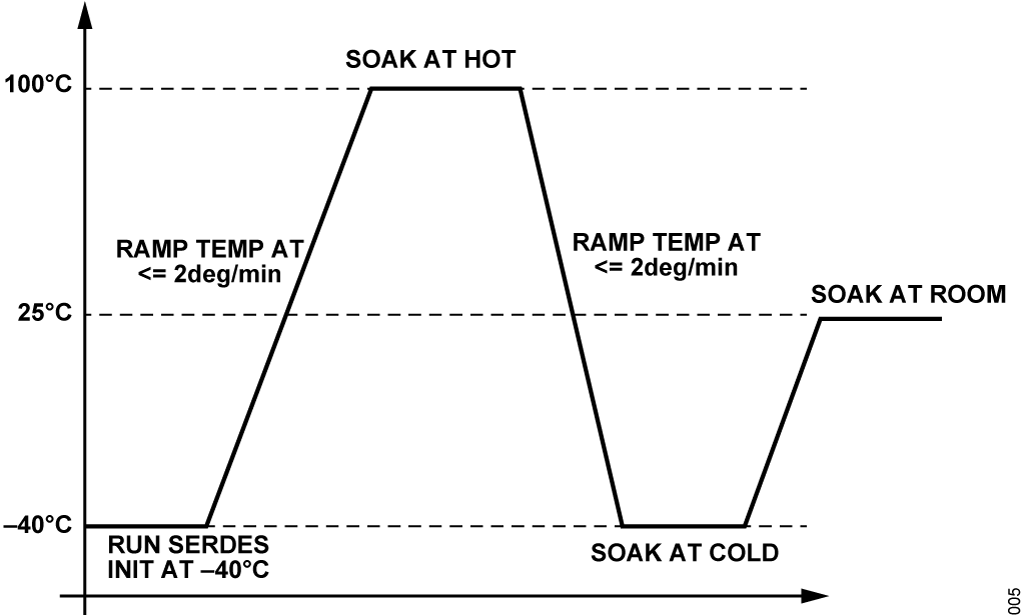
安定したリンクが実現され、そのリンクが良好な状態でチューニングは必要ないことを示すメトリクスが得られたら、温度変化に対するこのリンクの安定性を確認するためのテストを行う必要があります。通常は、一方の温度限界値でSERDES InitCalを実行してからもう一方の温度限界値へ移行し、その後室温に戻りますが、各温度点でデバイスをその温度に馴染ませる時間を取れるようにしてください温度プロファイルの例を図6 に示します。SerdesTrackingCalStatusGet() API を使用し、細かい温度間隔(例えば10ºC)でトラッキング・キャリブレーション・メトリクスを読み取ってファイルに保存し、SERDES メトリクス・リミットによる疑似コードのチェックのセクションに示すリミットに対してポストプロセシングを行うことができます。SERDES メトリクス・リミットによる疑似コードのチェックのセクションに示したものと同じリミット・チェックを使用できます。
SERDES の初期キャリブレーション時間
比較的単純なチューニング手順に加え、SERDES の初期キャリブレーション時間に対する改善点がいくつかあります。これらは、主に24.3G のレーン・レートに対するものです。相違の概要については表5 を参照してください。
| Use Case | Calibration Time | ≧ with Enhanced Tuning Feature |
| 32 G | N/A | N/A |
| 24 G | 7.7 sec | 12.5 sec |
| 19 G | 10.2 sec | 11.5 sec |
| 16 G | 6.4 sec | 12.1 sec |
SERDES 問題分析のためのARM ダンプ・シーケンス
リンク・チューニング・プロセスは、異なる温度と様々なSERDES レーン・レートで安定したSERDES 性能が得られるように、テストされた上で示されています。最初に水平方向のeyeSweep を実行することによって追加的なSERDES テレメトリ・データを保存し、高性能の縮小命令セット(RISC)コンピュータ(ARM)でダンプすることができます。しかし、まだ問題が残っていて、ADRV904x サポート・チームによる分析が更に必要なときは、以下のシーケンスに従ってテストを行ってください。
- SERDES の初期キャリブレーションを実行して、SERDES トラッキングをディスエーブルします。
- FPGA/BBICからPRBS パターンを送信します。ADRV904x のPRBS チェッカーをイネーブルします。
- RunEyeSweep_v2() を使って水平eyeSweep を実行し、DfrmPrbsCountReset()を使ってPRBS エラーをすべてクリアします。
- SERDES トラッキングをイネーブルします。
- 通常のテスト(例えば温度変化に対するテスト)を実行してPRBS エラーの有無を定期的にチェックし、エラーがある場合は以下を実行します。
- 垂直eyeSweep と水平eyeSweep を実行します。
- ARM ダンプを行います。
- ステップ5 に示すテストで一定時間PRBS エラーがない場合は、以下を実行します。
- 垂直eyeSweep と水平eyeSweep を実行します。
- ARM ダンプを行います。
ARM ダンプ分析は、少なくとも1 温度サイクル実行することを推奨します。これは、温度領域テレメトリが記録されるようにするためです。
PYTHON スクリプト:SERDES ヘルス・マトリックス
'''
Koror IronPython Programming Template Version 0.2
Generated with:
ACE GUI Version: 1.26.3240.1417
ACE Plug-in Vesion: 1.2023.42300
API Client Version: 2.9.0.4
API Server Version: 0.0.0.0
FPGA Version: 0.0.0.0
ARM Version: 0.0.0.0
StreamVersion: 2.9.0.4
Note: ACE does not need to be disconnected from ADRV9040 command server before running this script
anymore.
'''
import clr
import System
from System import Array, Boolean, SByte, Byte, Int16, UInt16, Int32, UInt32, Int64, UInt64
import sys
import os
import glob # for finding plug-in's installation path
import json, getpass, time
ACE_DIRECTORY = os.environ['ACEEXEDIR'] or os.getcwd()
""" str: path to ACE
Example: 'C:\Program Files\Analog Devices\ACE'
"""
CLIENT_DIRECTORY = os.environ['ADRV9040LIBPATH'] or (glob.glob(r'C:\ProgramData\Analog Devices\ACE\Plu►
gins\Board.ADRV904*')[0] + '\lib')
""" str: path to client DLLs included in ADRV9040 Board plugin's installation
Example: 'C:\ProgramData\Analog Devices\ACE\Plugins\Board.ADRV9040.1.2021.24400\lib'
"""
D0FAULT_IPADDRESS = '192.168.1.12'
DEFAULT_PORT = '5000'
# Add ACE and client to path
sys.path.append(ACE_DIRECTORY)
sys.path.append(CLIENT_DIRECTORY)
# Verify ADRV9040 plugin version used
print 'Loading client DLLs from', CLIENT_DIRECTORY
clr.AddReference("AnalogDevices.EvalClient")
clr.AddReference("AnalogDevices.EvalClient.Installers")
clr.AddReference("AnalogDevices.EvalClient.Adrvgen6.Ad9528.Device")
clr.AddReference("AnalogDevices.EvalClient.Adrvgen6.Board")
clr.AddReference("AnalogDevices.EvalClient.Adrvgen6.Device")
clr.AddReference("AnalogDevices.EvalClient.Adrvgen6.Fpga.Device")
clr.AddReference("AnalogDevices.EvalClient.Adrvgen6.Platform")
clr.AddReference("Adrv904x.Configurator")
clr.AddReference("StreamGen")
from AnalogDevices.EvalClient import *
from AnalogDevices.EvalClient.Installers import *
from AnalogDevices.EvalClient.Adrvgen6.Board import *
from AnalogDevices.EvalClient.Adrvgen6.Board.BaseClasses import *
from AnalogDevices.EvalClient.AD9528 import *
from AnalogDevices.EvalClient.Adrvgen6.Ad9528.Device import *
from AnalogDevices.EvalClient.Adrvgen6.Fpga.Device import *
from AnalogDevices.EvalClient.FPGAGEN6 import *
from AnalogDevices.EvalClient.Device import *
from AnalogDevices.EvalClient.AdiCommon import *
from AnalogDevices.EvalClient.Adrvgen6 import *
from AnalogDevices.Adrvgen6.Platform import *
from AnalogDevices.Adrv904x.Configurator import *
from Adi.Design import *
def connect(ipAddress="", portNumber=""):
"""
Connect IronPython to the command server.
If TCP connection exceptions are seen, please verify that
ACE is disconnected from the ADRV9040 command server (see header).
"""
ipAddress = ipAddress or DEFAULT_IPADDRESS
portNumber = portNumber or DEFAULT_PORT
print 'Attempting to connect to {}:{}...'.format(ipAddress, portNumber)
EvalClientManager.Instance.Initialize(CLIENT_DIRECTORY)
transport = Transports.CreateDefaultTcpTransport(ipAddress + ':' + portNumber)
context = ExecutionContext(transport)
context.ErrorRetriever = ErrorRetriever()
platform = EvalClientManager.Instance.PlatformBuilder.CreatePlatform('', context)
platform.Timeout = 60000
platform.OutputFilesBasePath = '.'
configGen = ConfigGen()
return platform
def spiWriteByte(address, data):
"""
>>> spiWriteByte(0xA, 0x55)
spiWriteByte 0x000A 0x55
"""
data = Array[Byte]([data])
numBytes = len(data)
adrv904x.hal.RegistersByteWrite(None, address, data, numBytes)
print 'spiWriteByte\t0x{:04X}\t0x{:02X}'.format(address, int(data[0]))
def spiReadByte(address, numBytes=1):
"""
>>> spiWriteByte(0xA, 0x55);
>>> spiReadByte(0xA)
spiReadByte 0x000A 0x55
85
"""
data = Array[Byte]([0])
adrv904x.hal.RegistersByteRead(None, address, data, None, numBytes)
data = int(data[0]) # get first element of returned data array
print 'spiReadByte\t0x{:04X}\t0x{:02X}'.format(address, data)
return data
def csvFileCreate(InitCal_outputFile, TrackingCal_outputFile):
titles_init = ["laneNumber", "lpfMask", "needTuning", "eyeWidth", "eyeHeight", "isTrackingCal",
"calStatus.temperature",
"calStatus.lpfIndex", "calStatus.ctleIndex", "calStatus.numEyes", "calStatus.bsum",
"calStatus.bsum_dc",
"calStatus.spoLeft", "calStatus.spoRight", "calStatus.eom", "calStatus.eomMax", "calStatus.pd",
"calStatus.innerUp", "calStatus.innerDown", "calStatus.outerUp", "calStatus.outerDown"]
for _i in range(8):
titles_init.append("calStatus.b[{0}]".format(_i))
with open(InitCal_outputFile, 'w') as f:
f.write(','.join(titles_init) + '\n')
titles_tracking = ["laneNumber", "lpfMask", "isTrackingCal", "calStatus.temperature", "calSta►
tus.pd[0]",
"calStatus.pd[1]",
"calStatus.dllPeakPd[0]", "calStatus.dllPeakPdDelta[0]", "calStatus.dllPeakPdDelta[1]",
"calStatus.innerUp", "calStatus.innerDown", "calStatus.outerUp", "calStatus.outerDown",
"calStatus.ps[0]",
"calStatus.ps[1]"]
for _i in range(8):
titles_tracking.append("calStatus.b[{0}]".format(_i))
for _i in range(16):
titles_tracking.append("calStatus.yVector[{0}]".format(_i))
with open(TrackingCal_outputFile, 'w') as f:
f.write(','.join(titles_tracking) + '\n')
def RunVerticalEyeSweep(lane, printLog=0):
print('**** Running vertical Eye Sweep V2 for Lane{0} ****'.format(lane))
runEyeVerticalSweep = adi_adrvgen6_CpuCmd_RunVertEyeSweep_t()
runEyeVerticalSweepResp = adi_adrvgen6_CpuCmd_RunVertEyeSweepResp_t()
runEyeVerticalSweep.lane = System.Enum.GetValues(adi_adrvgen6_CpuCmd_DeserializerLane_e)[lane]
adrv904x.dataInterface.RunVerticalEyeSweep_v2(runEyeVerticalSweep, runEyeVerticalSweepResp)
spo_p_list = runEyeVerticalSweepResp.eyeHeightsAtSpo[0:64:2]
spo_n_list = runEyeVerticalSweepResp.eyeHeightsAtSpo[1:64:2]
eyeHeightMax = 0
eyeWidth = 0
for spo_idx, spo_p, spo_n in zip(range(-15, 17), spo_p_list, spo_n_list):
eyeHeight = spo_p - spo_n
if (abs(spo_p) != 0x7F) | (abs(spo_n) != 0x7F):
if eyeHeight > eyeHeightMax:
eyeHeightMax = eyeHeight
if eyeHeight > 0:
eyeWidth += 1
if printLog:
print('{0}\t{1}\t{2}'.format(spo_idx, spo_p, spo_n))
if printLog:
print('\n### Printing Eye Diagram ###')
eye_graph = [' # ']*33
for y in range(127, -128, -1):
if y >= 0:
spo_list = spo_p_list
else:
spo_list = spo_n_list
for idx, val in enumerate(spo_list):
if abs(val) == 0x7F:
eye_graph[idx+1] = ' # '
elif abs(y) <= abs(val):
eye_graph[idx+1] = ' '
else:
eye_graph[idx+1] = ' # '
eye_graph[0] = '{: >4} |'.format(y)
print('\t'.join(eye_graph))
print('---- {0}'.format(''.join(['----']*32)))
print('spo \t{}\n'.format('\t'.join(['{:^3}'.format(x) for x in range(-15,17)])))
return eyeWidth, eyeHeightMax
#
def InitCalStatusGet(calget, channel, printLog=0):
CALGET = {
0x0001: adi_adrvgen6_InitCalibrations_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_IC_RX_DC_OFFSET,
0x0002: adi_adrvgen6_InitCalibrations_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_IC_ADC_RX,
0x0004: adi_adrvgen6_InitCalibrations_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_IC_ADC_ORX,
0x0008: adi_adrvgen6_InitCalibrations_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_IC_ADC_TXLB,
0x0010: adi_adrvgen6_InitCalibrations_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_IC_TXDAC,
0x0020: adi_adrvgen6_InitCalibrations_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_IC_TXBBF,
0x0040: adi_adrvgen6_InitCalibrations_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_IC_TXLB_FILTER,
0x0080: adi_adrvgen6_InitCalibrations_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_IC_TXLB_PATH_DLY,
0x0100: adi_adrvgen6_InitCalibrations_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_IC_TX_ATTEN_CAL,
0x0200: adi_adrvgen6_InitCalibrations_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_IC_HRM,
0x0400: adi_adrvgen6_InitCalibrations_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_IC_TXQEC,
0x0800: adi_adrvgen6_InitCalibrations_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_IC_TXLOL,
0x1000: adi_adrvgen6_InitCalibrations_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_IC_SERDES
}
CHANNEL = {
0x00: adi_adrvgen6_Channels_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_CHOFF, # /*!< No channels are enabled */
0x01: adi_adrvgen6_Channels_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_CH0, # /*!< Channel 0 enabled */
0x02: adi_adrvgen6_Channels_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_CH1, # /*!< Channel 1 enabled */
0x04: adi_adrvgen6_Channels_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_CH2, # /*!< Channel 2 enabled */
0x08: adi_adrvgen6_Channels_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_CH3, # /*!< Channel 3 enabled */
0x10: adi_adrvgen6_Channels_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_CH4, # /*!< Channel 4 enabled */
0x20: adi_adrvgen6_Channels_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_CH5, # /*!< Channel 5 enabled */
0x40: adi_adrvgen6_Channels_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_CH6, # /*!< Channel 6 enabled */
0x80: adi_adrvgen6_Channels_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_CH7 # /*!< Channel 7 enabled */
}
calStatus = adi_adrvgen6_CalStatus_t()
adrv904x.cals.InitCalStatusGet(CALGET.get(calget), CHANNEL.get(channel), calStatus)
if (printLog):
print('### InitCalStatusGet() ###')
print("InitCal percentComplete = %d" % calStatus.percentComplete)
print("InitCal performanceMetric = %d" % calStatus.performanceMetric)
print("InitCal iterCount = %d" % calStatus.iterCount)
print("InitCal updateCount = %d" % calStatus.updateCount)
print("InitCal errorCode = %d\n" % calStatus.errorCode)
def cals_TrackingCalStatusGet(calId, channel, printLog):
TrackCalID = {
1: adi_adrvgen6_TrackingCalibrationMask_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_TC_RX_QEC_MASK ,
2: adi_adrvgen6_TrackingCalibrationMask_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_TC_TX_LOL_MASK ,
4: adi_adrvgen6_TrackingCalibrationMask_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_TC_TX_QEC_MASK ,
8: adi_adrvgen6_TrackingCalibrationMask_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_TC_TX_SERDES_MASK ,
16:adi_adrvgen6_TrackingCalibrationMask_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_TC_RX_ADC_MASK ,
32:adi_adrvgen6_TrackingCalibrationMask_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_TC_TX_LB_ADC_MASK ,
64:adi_adrvgen6_TrackingCalibrationMask_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_TC_ORX_ADC_MASK
}
CHANNEL = {
0x00 : adi_adrvgen6_Channels_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_CHOFF ,# /*!< No channels are enabled */
0x01 : adi_adrvgen6_Channels_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_CH0 ,# /*!< Channel 0 enabled */
0x02 : adi_adrvgen6_Channels_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_CH1 ,# /*!< Channel 1 enabled */
0x04 : adi_adrvgen6_Channels_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_CH2 ,# /*!< Channel 2 enabled */
0x08 : adi_adrvgen6_Channels_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_CH3 ,# /*!< Channel 3 enabled */
0x10 : adi_adrvgen6_Channels_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_CH4 ,# /*!< Channel 4 enabled */
0x20 : adi_adrvgen6_Channels_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_CH5 ,# /*!< Channel 5 enabled */
0x40 : adi_adrvgen6_Channels_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_CH6 ,# /*!< Channel 6 enabled */
0x80 : adi_adrvgen6_Channels_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_CH7 # /*!< Channel 7 enabled */
}
calStatus = adi_adrvgen6_CalStatus_t()
adrv904x.cals.TrackingCalStatusGet(TrackCalID.get(calId), CHANNEL.get(channel), calStatus)
if (printLog):
print('### TrackingCalStatusGet() ###')
print("TrackingCal percentComplete = %d" % calStatus.percentComplete)
print("TrackingCal performanceMetric = %d" % calStatus.performanceMetric)
print("TrackingCal iterCount = %d" % calStatus.iterCount)
print("TrackingCal updateCount = %d" % calStatus.updateCount)
print("TrackingCal errorCode = %d\n" % calStatus.errorCode)
def SerdesInitCalStatusGet(laneNumber, printLog=0, writeToCsvFile=0, csvFileName='', lpfMask=0, eye►
Width=0, eyeHeight=0):
filepath = adi_adrvgen6_GenericStrBuf_t()
filename = "init_cal_status_log.txt"
for _i in range(len(filename)):
filepath.c_str[_i] = ord(filename[_i])
msg = adi_adrvgen6_GenericStrBuf_t()
msgName = "output"
for _i in range(len(msgName)):
msg.c_str[_i] = ord(msgName[_i])
calStatus = adi_adrvgen6_SerdesInitCalStatus_t()
adrv904x.dataInterface.SerdesInitCalStatusGet(filepath, laneNumber, msg, calStatus)
needTuning = Serdes_health_check(calStatus) # run the health check by running limit checks on some of
the parameters.
if (printLog):
# log the return value from above API function call to the output dictionary - optional
print('### SerdesInitCalStatusGet() ###')
print('Serdes InitCal data for Lane{}'.format(laneNumber))
print('calStatus.temperature = {}'.format(calStatus.temperature))
print('calStatus.lpfIndex = {}'.format(calStatus.lpfIndex))
print('calStatus.ctleIndex = {}'.format(calStatus.ctleIndex))
print('calStatus.numEyes = {}'.format(calStatus.numEyes))
print('calStatus.bsum = {}'.format(calStatus.bsum))
print('calStatus.bsum_dc = {}'.format(calStatus.bsum_dc))
print('calStatus.spoLeft = {}'.format(calStatus.spoLeft))
print('calStatus.spoRight = {}'.format(calStatus.spoRight))
print('calStatus.eom = {}'.format(calStatus.eom))
print('calStatus.eomMax = {}'.format(calStatus.eomMax))
print('calStatus.pd = {}'.format(calStatus.pd))
print('calStatus.innerUp = {}'.format(calStatus.innerUp))
print('calStatus.innerDown = {}'.format(calStatus.innerDown))
print('calStatus.outerUp = {}'.format(calStatus.outerUp))
print('calStatus.outerDown = {}'.format(calStatus.outerDown))
for idx, val in enumerate(calStatus.b):
print('HC_IC_b{} = {}'.format(idx, val))
print('')
if (writeToCsvFile):
isTrackingCal = 0 # just a flag to denote if writing tracking cal status or InitCal status
metricData = [laneNumber, lpfMask, needTuning, eyeWidth, eyeHeight, isTrackingCal, calStatus.tempera►
ture,
calStatus.lpfIndex, calStatus.ctleIndex, calStatus.numEyes, calStatus.bsum, calStatus.bsum_dc,
calStatus.spoLeft, calStatus.spoRight, calStatus.eom, calStatus.eomMax, calStatus.pd,
calStatus.innerUp, calStatus.innerDown, calStatus.outerUp, calStatus.outerDown]
for val in calStatus.b:
metricData.append(val)
with open(csvFileName, 'a') as f:
f.write(','.join([str(x) for x in metricData])+'\n')
return calStatus, needTuning
def SerdesTrackingCalStatusGet(laneNumber, printLog=0, writeToCsvFile=0, csvFileName='', lpfMask=0):
filepath = adi_adrvgen6_GenericStrBuf_t()
filename = "tracking_cal_status_log.txt"
for _i in range(len(filename)):
filepath.c_str[_i] = ord(filename[_i])
msg = adi_adrvgen6_GenericStrBuf_t()
msgName = "output"
for _i in range(len(msgName)):
msg.c_str[_i] = ord(msgName[_i])
calStatus = adi_adrvgen6_SerdesTrackingCalStatus_t()
adrv904x.dataInterface.SerdesTrackingCalStatusGet(filepath, laneNumber, msg, calStatus)
if printLog:
print('### SerdesTrackingCalStatusGet() ###')
print('Serdes TrackingCal data for Lane{}'.format(laneNumber))
print('calStatus.temperature = {}'.format(calStatus.temperature))
print('calStatus.pd[0] = {}'.format(calStatus.pd[0]))
print('calStatus.pd[1] = {}'.format(calStatus.pd[1]))
print('calStatus.dllPeakPd[0] = {}'.format(calStatus.dllPeakPd[0]))
print('calStatus.dllPeakPd[1] = {}'.format(calStatus.dllPeakPd[1]))
print('calStatus.dllPeakPdDelta[0] = {}'.format(calStatus.dllPeakPdDelta[0]))
print('calStatus.dllPeakPdDelta[1] = {}'.format(calStatus.dllPeakPdDelta[1]))
print('calStatus.innerUp = {}'.format(calStatus.innerUp))
print('calStatus.innerDown = {}'.format(calStatus.innerDown))
print('calStatus.outerUp = {}'.format(calStatus.outerUp))
print('calStatus.outerDown = {}'.format(calStatus.outerDown))
print('calStatus.ps[0] = {}'.format(calStatus.ps[0]))
print('calStatus.ps[1] = {}'.format(calStatus.ps[1]))
for idx, val in enumerate(calStatus.b):
print('HC_TC_b{} = {}'.format(idx, val))
for idx, val in enumerate(calStatus.yVector):
print('HC_TC_yVector{} = {}'.format(idx, val))
print('')
if writeToCsvFile:
isTrackingCal = 1 # just a flag to denote if writing tracking cal status or InitCal status
metricData = [laneNumber, lpfMask, isTrackingCal, calStatus.temperature, calStatus.pd[0], calSta►
tus.pd[1],
calStatus.dllPeakPd[0], calStatus.dllPeakPdDelta[0], calStatus.dllPeakPdDelta[1],
calStatus.innerUp, calStatus.innerDown, calStatus.outerUp, calStatus.outerDown, calStatus.ps[0],
calStatus.ps[1]]
for val in calStatus.b:
metricData.append(val)
for val in calStatus.yVector:
metricData.append(val)
with open(csvFileName, 'a') as f:
f.write(','.join([str(x) for x in metricData])+'\n')
return calStatus
def Serdes_health_check(calStatus):
check_sat = check_isi = check_horizontal = check_postCursors = 0
if (abs(calStatus.outerUp) >= 63 | abs(calStatus.outerDown) >= 63):
check_sat = 1
print('DFE is near saturation, consider lowering LPF bandwidth or incident signal swing')
if (abs(float(calStatus.b[1]) / float(calStatus.b[0])) < 0.1):
check_isi = 1
print('ISI on channel is too low, consider increasing ISI by lowering CTLE LPF bandwidth')
if ((calStatus.spoLeft < 5) | (calStatus.spoRight < 5)):
check_horizontal = 1
print('Horizontal eye opening is too low, consider raising FPGA JTx signal swing or increasing CTLE
LPF bandwidth')
if (abs(calStatus.b[3]) | abs(calStatus.b[4]) | abs(calStatus.b[5]) | abs(calStatus.b[6])) >= 8:
check_postCursors=1
print ('Post cursor on channel is higher than expected, consider lowering CTLE LPF bandwidth')
if (check_sat | check_isi | check_horizontal | check_postCursors) == 1:
print('Tuning needed\n')
else:
print('no tuning needed\n')
return (check_sat | check_isi | check_horizontal)
def programBoard(filepath, rsFilePath=''):
resourceFolder = r'C:\Users\{}\AppData\Local\Analog Devices\ACE\PluginFiles\Board.ADRV9040\Local'.for►
mat(
getpass.getuser())
print('Loading profile from {}...'.format(filepath))
initStruct = AdrvGen6ProgramSupport()
initStruct = initStruct.ProgramSupportRead(filepath)
syncSettings = AdrvGen6FileSyncSettings()
syncSettings.host = DEFAULT_IPADDRESS
syncSettings.username = 'root'
syncSettings.password = 'analog'
syncSettings.srcDir = resourceFolder
syncSettings.dstDir = '/home/analog/adrv9040_server/data'
# Set resource file generation options
programOptions = AdrvGen6ProgramOptions()
programOptions.GenerateCStructure = False
programOptions.GenerateCpuProfile = True
programOptions.GenerateStream = True
programOptions.GenerateRadioSequencer = False
if rsFilePath != '':
programOptions.GenerateRadioSequencer = True
initStruct.rsGeneratorSettings = rsFilePath
print("Programming...please wait...")
START_TIME = time.time()
board.Program(initStruct, AdrvGen6ProgramActionMask.ALL_PHASES, syncSettings, programOptions)
DURATION = time.time() - START_TIME
print("Device Fully Programmed successfully in {:.2f}s!\n".format(DURATION))
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Connect IronPython to command server
platform = connect()
# Get device objects
board = platform.Boards[0]
ad9528Dev = board.DeviceGet('ad9528', 0)
fpgaDev = board.DeviceGet('fpga', 0)
try:
adrv904x = board.DeviceGet('adrvgen6', 0)
except SystemError: # SW0.5 onwards
adrv904x = board.Adrvgen6DeviceGet(0)
# API documentation: System Explorer -> ADRV904X -> Open Help File
# Check SPI functionality by writing/reading from scratchpad SPI register
address = 0xA
data = 0x55
spiWriteByte(address, data)
spiReadByte(address)
# Your code goes here!
print 'Hello World!'
# *********************************** INPUT VARIABLES
**************************************************
uc_json_inputFile = r'C:\Temp\input.json'
RS_json_inputFile = r'' # If RS in not enabled, use blank string
SerdesInitCalStatusGet_outputFile = r'C:\temp\JESD_Enhanced_Tuning\_init.csv'
SerdesTrackingCalStatusGet_outputFile = r'C:\temp\JESD_Enhanced_Tuning\_tracking.csv'
printLog = 0
writeToCsvFile = 1
#
*******************************************************************************************************
needTuning = [0]*8
# Create the labels for the output files
if writeToCsvFile:
csvFileCreate(SerdesInitCalStatusGet_outputFile, SerdesTrackingCalStatusGet_outputFile)
# Program the board and load the JSON file
programBoard(uc_json_inputFile, RS_json_inputFile)
time.sleep(20) # Need to wait some time before calling the APIs, otherwise it gives errors
with open(uc_json_inputFile, 'r') as f:
fileData = f.readlines()
for idx, line in enumerate(fileData): # Loop to remove comments in JSON file
if line.__contains__('//'):
fileData[idx] = line.split('//')[0]
json_file = json.loads(''.join(fileData))
# Check which deframer lanes are enable
deframerStatus = adi_adrvgen6_DeframerStatus_v2_t()
adrv904x.dataInterface.DeframerStatusGet_v2(adi_adrvgen6_DeframerSel_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_DEFRAMER_0, defra►
merStatus )
phyLaneMask = deframerStatus.phyLaneMask
adrv904x.dataInterface.DeframerStatusGet_v2(adi_adrvgen6_DeframerSel_e.ADI_ADRVGEN6_DEFRAMER_1, defra►
merStatus )
phyLaneMask = phyLaneMask | deframerStatus.phyLaneMask
print('phyLaneMask = {}'.format(hex(int(phyLaneMask))))
deframerLanesEnable = [(phyLaneMask >> bit) & 0x1 for bit in range(8)]
print 'deframerLanesEnable',deframerLanesEnable
# Check the configuration of the selected deframer lanes
for lane, enbl in enumerate(deframerLanesEnable):
if enbl:
if json_file["configSettings"]["Jesd204"]["deser_lane_cfg"][lane]["highBoost"] != 1:
print('highBoost should be set to "1" but it is "{}" in the json file'.format(json_file["configSet►
tings"]["Jesd204"]["deser_lane_cfg"][lane]["highBoost"]))
lpfMask = json_file["configSettings"]["Jesd204"]["deser_lane_cfg"][lane]["configOption1"]
print 'lpfMask',lpfMask
laneMask = 1 << lane
(eyeWidth, eyeHeight) = RunVerticalEyeSweep(lane, printLog)
InitCalStatusGet(0x1000, laneMask, printLog) # will see InitCal updateCount increment each time you
run Serdes InitCal unless you mask off a particular lane
cals_TrackingCalStatusGet(0x8, laneMask, printLog)
InitcalStatus, needTuning[lane] = SerdesInitCalStatusGet(lane, printLog, writeToCsvFile, SerdesInitCal►
StatusGet_outputFile, lpfMask, eyeWidth, eyeHeight)
TrackingcalStatus = SerdesTrackingCalStatusGet(lane, printLog, writeToCsvFile, SerdesTrackingCalStatus►
Get_outputFile, lpfMask) # could monitor tracking metrics vs. temp and log periodically
print('Re-tuning needed per lane: {}'.format(needTuning))
ymore.
'''
API 機能
InitCal ステータスおよびTrackingCalStatus ヘルス・メトリクスAPI によって返されるすべてのパラメータの概要を、表6 と表7に示します。なお、それ以上のリンク・チューニングが必要かどうかを判断するためにチェックする必要があるのは、これらのパラメータの一部だけです。
| InitCal ステータス取得フィールド | 基本的な説明 |
| InitCalStatus.temperature | initCal を実行する温度。 |
| InitCalStatus.lpfIndex | LPF テーブルで選択したLPF エントリのインデックス。 |
| InitCalStatus.ctleIndex | CTLE テーブルで選択したCTLE エントリのインデックス。 |
| InitCalStatus.numEyes | アイを開くことができるCTLE エントリの数。 |
| InitCalStatus.bsum | Bsum は信号のピーク値を反映します。 |
| InitCalStatus.bsum_dc | Bsum_dc は信号のDC 値です。 |
| InitCalStatus.spoLeft | アイ開口部の左側にある位相の数。spoLeft + spoRight は水平方向のeyeWidth を与えます。 |
| InitCalStatus.spoRight | アイ開口部の右側にある位相の数。spoLeft + spoRight は水平方向のeyeWidth を与えます。 |
| InitCalStatus.eom | アイの開口状態を示すメトリクスで、アイの面積を表します。 |
| InitCalStatus.eomMax | アイの開口状態を示すメトリクスの最大値。 |
| InitCalStatus.pd | ロック点におけるフェーズ・ディテクタの値。 |
| InitCalStatus.innerUp | 値(1 − b1)。この値はフェーズ・ディテクタの値に近くなければなりません。 |
| InitCalStatus.innerDown | 値−(1 − b1)。 |
| InitCalStatus.outerUp | 値(1 + b1)。この値は最大信号振幅に相当します(b の値がすべて正の場合)。 |
| InitCalStatus.outerDown | 値(1 + b1)。 |
| InitCalStatus.b[7:0] | DFE が計算したカーソル前後のb の値。これらは、ISI を除去するためにデシジョン・フィードバック・イコライザで使われます。 |
| TrackingCal ステータス取得フィールド | 基本的な説明 |
| TrackingCalStatus.temperature | 最後のトラッキング・キャリブレーションが行われた温度 |
| TrackingCalStatus.pd[0] | レーン・スライス0 のフェーズ・ディテクタ値 |
| TrackingCalStatus.pd[1] | レーン・スライス1 のフェーズ・ディテクタ値 |
| TrackingCalStatus.dllPeakPd[0] | レーンのスライス0 の遅延ロック・ループ(DLL)曲線のピーク値 |
| TrackingCalStatus.dllPeakPd[1] | レーンのスライス1 のDLL 曲線のピーク値 |
| TrackingCalStatus.dllPeakPdDelta[0] | レーンのスライス0 のロック点におけるDLL ピーク値とDLL フェーズ・ディテクタ値の差 |
| TrackingCalStatus.dllPeakPdDelta[1] | レーンのスライス1 のロック点におけるDLL ピーク値とDLL フェーズ・ディテクタ値の差 |
| TrackingCalStatus.innerUp | 表6 のinitCalStatus を参照 |
| TrackingCalStatus.innerDown | 表6 のinitCalStatus を参照 |
| TrackingCalStatus.outerUp | 表6 のinitCalStatus を参照 |
| TrackingCalStatus.outerDown | 表6 のinitCalStatus を参照 |
| TrackingCalStatus.ps[0] | 不等間隔サンプリングの最初のサンプリング点における位相オフセット |
| TrackingCalStatus.ps[1] | 不等間隔サンプリングの2 番目のサンプリング点における位相オフセット |
| TrackingCalStatus.b[7:0] | DFE が計算したカーソル前後のb の値。これらは、ISI を除去するためにデシジョン・フィードバック・イコライザで使われます。 |
| TrackingCalStatus.yVector[15:0] | 不等間隔サンプリングの2 つのサンプリング点に相当するb の値 |