Understanding the Operation of the Frequency Synthesizer in Maxim’s RF Transceivers
Understanding the Operation of the Frequency Synthesizer in Maxim’s RF Transceivers
Abstract
The application note shows how to calculate the appropriate integer and fractional divider values for any desirable LO frequency that uses different reference frequencies (i.e., 19.2MHz, 20.72MHz, etc.). It tells the relationship between these two frequencies for five different Maxim’s RF transceivers.
Introduction
All of Maxim's 2.4GHz to 6GHz highly integrated transceivers include a high performance fractional-N synthesizer for generating the local oscillator (LO) signal. The fractional-N synthesizer generally consists of a phase locked loop with resolution as high as 20 bit, and integrated broadband voltage controlled oscillators (VCO's). The only additional components needed to generate the high performance LO are the reference input and passive loop filter. With the on-chip crystal oscillator, these transceivers can support both crystal and TCXO reference.
Traditional wireless data applications, such as Wi-Fi® and WiMAX®, use 20MHz and 40MHz reference input; therefore, most of the control software were designed with these default reference values. For applications that use different reference frequencies (i.e., 19.2MHz, 30.72MHz, etc.), users must bypass the graphical interface of the control software and enter the appropriate integer and fractional divider values directly into the register table for a given reference input frequency. This application note shows how to calculate the appropriate integer and fractional divider values for any desirable LO frequency and reference frequency. It tells the relationship between these two frequencies for five different Maxim RF transceivers. The specific frequency synthesizer parameters and register bits used to control these parameters are also shown. Every section is supported by an example to show how the registers are set.
RF Synthesizer
Block Diagram
The RF frequency synthesizer is a negative feedback control system which consists of a reference, phase frequency detector (PFD), charge pump, loop filter, voltage controlled oscillator (VCO), N counter, and RF output divider/multiplier (Figure 1). The high frequency VCO tracks the stable low frequency reference in frequency and phase by comparing the divided down VCO output to the reference input through the PFD. The output of the PFD is fed into the charge pump which then generates a current output proportional to the error. The current is converted into a voltage with the help of the loop filter, which then modulates the tune voltage of the VCO. Lastly to mitigate VCO pulling, there are usually multipliers and dividers between the VCO output and LO input to the mixers.

Figure 1. Frequency synthesizer block diagram.
MAX2829 Synthesizer
Block Diagram

Figure 2. MAX2829 synthesizer block diagram.
Synthesizer Specifications
- Typical Charge-Pump Frequency FPFD = 20MHz
- Reference Input Frequency Range FREF = 20MHz to 44MHz
- R Divider: 3 bits
- Range = 1 to 4
- Register 5, Bits D3:D1
| D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 | D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| R[3] | R[2] | R[1] |
- Integer Divider Ratio: 8 bits
- Register 3, D7:D0
| D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 | D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| N[8} | N[7] | N[6] | N[5] | N[4] | N[2] | N[2] | N[1] |
- Fractional Divider Ratio: 16 bits
- Register 4, D13:D0
| D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 | D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| F[16] | F[15] | F[14] | F[13] | F[12] | F[11] | F[10] | F[9] | F[8] | F[7] | F[6] | F[5] | F[4] | F[3] |
- Register 3, D12:D13
| D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 | D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| F[1] | F[2] |
Frequency Calculation Formula
LO Frequency Calculation:

Frequency Resolution:
In Integer Mode:
Min Frequency Step

In Fractional Mode:
Min Frequency Step
Example Register Settings
Below is an example to find out the values of Integer and Fractional divider ratio registers for a particular set of conditions.
Let's assume:
FREF = 26MHz and the desired FLO = 2450MHz, Set R =1
Divider Ratio 
Therefore:
N = 125 (d) = 10100011
F = 0.641025641 (d) = 1010010000011010
Download the "VCO_PLL_Calculation_for_Transceivers" excel file as a tool to calculate the values for N and F registers.
MAX2830/MAX2831/MAX2832 Synthesizer
Block Diagram

Figure 3. MAX2830/MAX2831/MAX2832 synthesizer block diagram.
Synthesizer Specifications
- Typical Charge-Pump Frequency FPFD = 20MHz
- Reference Input Frequency Range FREF = 20MHz to 44MHz
- R Divider: 1 bit
- Range = ÷ 1 or ÷ 2
- Register 5, Bit D2
| D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 | D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| R[1] |
- Integer Divider Ratio: 8 bits
- Register 3, D7:D0
| D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 | D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| N[8] | N[7] | N[6] | N[5] | N[4] | N[3] | N[2] | N[1] |
- Fractional Divider Ratio: 20 bits
- Register 4, D13:D0
| D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 | D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| F[20] | F[19] | F[18] | F[17] | F[16] | F[15] | F[14] | F[13] | F[12] | F[11] | F[10] | F[9] | F[8] | F[7] |
- Register 3, D13:D8
| D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 | D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| F[6] | F[5] | F[4] | F[3] | F[2] | F[1] |
Frequency Calculation Formula
LO Frequency Calculation:
 |
Frequency Resolution:
In Integer Mode:
Min Frequency Step
In Fractional Mode:
Min Frequency Step
Example Register Settings
Below is an example to find out the values of Integer and Fractional divider ratio registers for a particular set of conditions.
Let's assume:
FREF = 26MHz and the desired FLO = 2450MHz, set R = 1.
Divider Ratio

Therefore,
N = 94 (d) = 01011110
F = 0.23076923 (d) = 00111011000100111011
Download the "VCO_PLL_Calculation_for_Transceivers" excel file as a tool to calculate the values for N and F registers.
MAX2837 Synthesizer
Block Diagram

Figure 4. MAX2837 synthesizer block diagram.
Synthesizer Specifications
- Typical Charge-Pump Frequency Range FPFD = 11MHz to 40MHz
- Reference Input Frequency Range FREF = 20MHz to 44MHz
- R divider: 2 bits
- Range = ÷ 1, ÷ 2, ÷ 4, ÷ 8
- Register 20, Bits D2:D1
| D9 | D8 | D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| R[2] | R[1] |
- Integer Divider Ratio: 8 bits
- Register 19, D7:D0
| D9 | D8 | D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| N[8] | N[7] | N[6] | N[5] | N[4] | N[3] | N[2] | N[1] |
- Fractional Divider Ratio: 20 bits
- Register 18, D9:D0 , MSBs
| D9 | D8 | D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| F[20] | F[19] | F[18] | F[17] | F[16] | F[15] | F[14] | F[13] | F[12] | F[11] |
- Register 17, D9:D0, LSBs
| D9 | D8 | D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| F[10] | F[9] | F[8] | F[7] | F[6] | F[5] | F[4] | F[3] | F[2] | F[1] |
Frequency Calculation Formula
LO Frequency Calculation:

Frequency Resolution:
In Integer Mode:
Min Frequency Step
In Fractional Mode:
Min Frequency Step
Example Register Settings
Below is an example to find out the values of Integer and Fractional divider ratio registers for a particular set of conditions.
Let's assume:
FREF = 26MHz and the desired FLO = 2450MHz, set R = 2 since the FPFD is still in the typical range.
Divider Ratio
N = 251 (d) = 11111011
F = 0.2820513(d) = 01001000001101001000
Download the "VCO_PLL_Calculation_for_Transceivers" excel file as a tool to calculate the values for N and F registers.
MAX2850/MAX2851 Synthesizer
Block Diagram
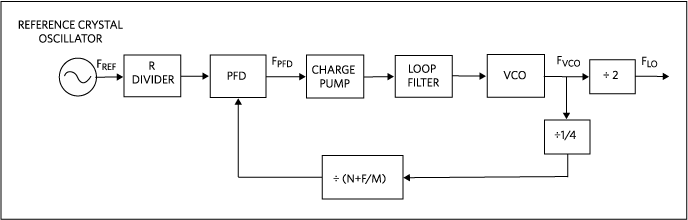
Figure 5. MAX2850/MAX2851 synthesizer block diagram.
Synthesizer Specifications
- Typical Charge-Pump Frequency FPFD = 40MHz
- Typical Reference Input Frequency FREF = 40MHz
- R divider: 2 bits
- Range = ÷ 1, ÷ 2, ÷ 4, ÷ 8
- Register 18, Bits D9:D8
| D9 | D8 | D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| R[2] | R[1] |
- Integer Divider Ratio: 8 bits
- Register 15, D7:D0
| D9 | D8 | D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| N[8] | N[7] | N[6] | N[5] | N[4] | N[3] | N[2] | N[1] |
- Fractional Divider Ratio: 20 bits
- Register 16, D9:D0 , MSBs
| D9 | D8 | D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| F[20] | F[19] | F[18] | F[17] | F[16] | F[15] | F[14] | F[13] | F[12] | F[11] |
- Register 17, D9:D0, LSBs
| D9 | D8 | D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| F[10] | F[9] | F[8] | F[7] | F[6] | F[5] | F[4] | F[3] | F[2] | F[1] |
Frequency Calculation Formula
LO Frequency Calculation:

Frequency Resolution:
In Integer Mode:
Min Frequency Step 
In Fractional Mode:
Min Frequency Step 
Example Register Settings
Below is an example to find out the values of Integer and Fractional divider ratio registers for a particular set of conditions.
Let's assume:
FREF = 32MHz and the desired FLO = 5380MHz, set R = 1.
Divider Ratio 
N = 84 (d) = 01010100
F = 0.0625 (d) = 0001 000000000000000000
Download the "VCO_PLL_Calculation_for_Transceivers" excel file as a tool to calculate the values for N and F registers.